Integration
Integrating with the Anchor Platform for facilitating cross-border payments involves implementing the following, at a minimum:
GET /customer&PUT /customerKYC API endpoints to request & collect customers' KYC dataGET /rateRFQ API endpoint to provide FX rates between the on & off-chain assets supportedGET /transactionsrequests to fetch updates on the Anchor Platform's transactions' statuses (documentation coming soon)JSON-RPCrequests to update the Anchor Platform's transactions' statuses
The following may also be required depending on your use case:
DELETE /customerif your business wants or is required to allow senders to request deletion of customer data
Create a Business Server
First, lets create a business server and add it to our docker compose file.
- YAML
version: "3.8"
services:
sep-server:
image: stellar/anchor-platform:latest
command: --sep-server
env_file:
- ./dev.env
volumes:
- ./config:/home
ports:
- "8080:8080"
depends_on:
- db
platform-server:
image: stellar/anchor-platform:latest
command: --platform-server
env_file:
- ./dev.env
volumes:
- ./config:/home
ports:
- "8085:8085"
depends_on:
- db
server:
build: .
ports:
- "8081:8081"
env_file:
- ./dev.env
db:
image: postgres:14
ports:
- "5432:5432"
env_file:
- ./dev.env
Next, create a simple web server using your preferred programming language and a Dockerfile that starts the server. docker compose up should successfully start all three services.
This guide does not provide an example implementation of the endpoints, but you can find more information about the request and response schemas in the Anchor Platform API Reference, and the sections below will expand on concepts important to understand when implementing the endpoints.
Customer Callback Endpoints
The Anchor Platform never stores your customers' PII, and instead acts as a proxy server between client applications and your business, forwarding requests and responses to the other party. Currently, requests and responses are almost identical to those defined in the SEP-12 KYC API specification.
Identifying Customers
Customers can be identified using two approaches.
The first approach uses a Stellar account and memo. When using the Anchor Platform for facilitating cross-border payments, the sending organization uses their own Stellar account, the one used to authenticate via SEP-10 Stellar Authentication, when registering customers with your business. Memos are used to distinguish unique customers originating from the same sending organization.
The second approach uses customer IDs generated by your service. For example, if a sending organization is registering a customer, your business will receive a PUT /customer request like the following:
- JSON
{
"account": "GDJUOFZGW5WYBK4GIETCSSM6MTTIJ4SUMCQITPTLUWMQ6B4UIX2IEX47",
"memo": "780284017",
"type": "sep31-sender",
"first_name": "John",
"last_name": "Doe",
"email": "[email protected]"
}
In this example, the GDJ...X47 public key identifies the sending organization, and the 780284017 memo identifies the customer. Memos are usually 64-bit integers, but they can also be other data types, so they should be saved as strings. In response, your business should return a customer ID.
- JSON
{
"id": "fb5ddc93-1d5d-490d-ba5f-2c361cea41f7"
}
Your business server can use any identifer for customers as long as it is a string.
Following the registration of a customer, the sending organization can use either approach when checking the customer's status. For example, you may get a GET /customer request like the following:
- Example
/customer?account=GDJUOFZGW5WYBK4GIETCSSM6MTTIJ4SUMCQITPTLUWMQ6B4UIX2IEX47&memo=780284017&type=sep31-sender
Or, the sending organziation could use the identifier you returned when they originally registered the customer.
- Example
/customer?id=fb5ddc93-1d5d-490d-ba5f-2c361cea41f7&type=sep31-sender
Your business will need to maintain a mapping between the account & memo used to originally register the customer and the ID you return in the response, as well as the KYC data provided. In future iterations of the Anchor Platform, we may maintain this mapping for your business so you only have to work with the IDs you generate.
Customer Types
Your business likely requires different sets of KYC information depending on the type of customer. You can define the labels for each of these customer types in your dev.assets.yaml file, and your sending organizations will need to understand which label to use when registering or querying the status of customers.
In PUT /customer requests, you should use the type passed to evaluate whether the sender has provided all of the required fields. In GET /customer requests, you should use the type to determine the customer's status.
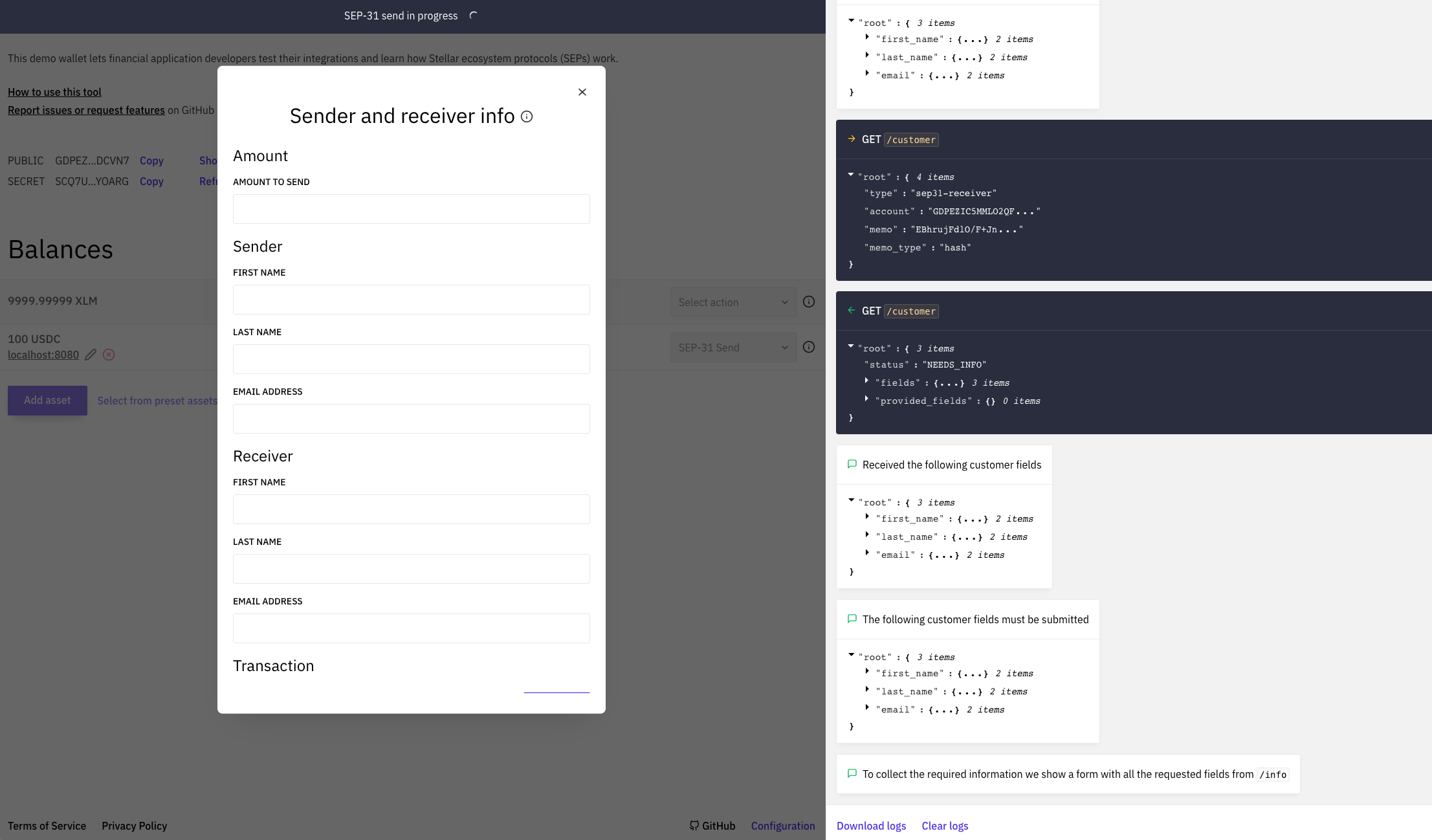
Test with the Demo Wallet
You can test your implementation with the Stellar Demo Wallet following the steps below.
- Select "Generate keypair for new account"
- Select "Create account"
- Select "Add Asset" and enter the asset code and the Anchor Platform's home domain,
localhost:8080 - Select "Add trustline"
- Fund your account with a balance of the asset
- Select "SEP-31 Send" in the dropdown menu
You should see the demo wallet find your service URLs, authenticate, and check which KYC fields it needs to collect. It should then present a form for you to enter the KYC details for the sender and reciever.
Once you've entered in the information requested, it will send that information to the Anchor Platform, which will send it to your business server. Once the demo wallet has the customers' IDs you generated, it will initiate a transaction which should fail.
Rate Callback Endpoint
Once the sending organization has registered the customers involved in the transaction, it will need to request a quote, or FX rate, from your business. The Anchor Platform requests this information from your business server using the GET /rate endpoint.
Firm vs. Indicative Quotes
Requests for quotes will have a type parameter that is either indicative or firm. If type=firm, your response must include the id & expires_at date-time field and reserve the liquidity needed to fulfil this quote until the quote expires. If type=indicative, do not return id or expires_at fields because the rate provided will not be used in a transaction.
Note that the client may request that the quote expires after a specific date-time using the expires_after parameter. Your business must honor this request by returning an expires_at value that is at or after the requested date-time or reject the request with a 400 Bad Request response, which will be forwarded to the client.
Using the Client ID
Requests may include a client_id parameter that identifies the sending organization requesting the rate. You can use this parameter to adhere to the commercial terms agreed upon with that sending organization, such as offering discounted rates. client_id may not be present for indicative requests, in which case your market price should be returned. Currently client_id will always be the Stellar public key the sending organization used to authenticate with the Anchor Platform.
Delivery Methods
It is common for businesses' rates and fees to differ depending on the payment rails used to send funds to the recipient. If your delivery methods are configured in your asset.yaml file, clients will always provide the payment rail they want your business to use for firm quote requests.
Because this endpoint is currently only used paying out remittances in off-chain assets, the buy_delivery_method will be used. If this endpoint is ever used in other transaction flows such as SEP-24 deposits, then sell_delivery_method may also be passed for business that support these types of transactions.
Fetching Transaction Status Updates
To facilitate cross-border payments, you'll need to be able to detect when a sending organization has sent your business an on-chain payment and determine which transaction that payment was meant to fulfil.
The easiest way to do that is to run the Stellar Observer, which will detect these payments and update the corresponding transaction record with information about the payment. Your business can then detect these updates by polling the GET /transactions Platform API endpoint.
Running the Stellar Observer
The Stellar Observer monitors the Stellar ledger for payments made to your account(s) and updates the corresponding transaction records with on-chain payment information. To run the observer, add the following to your docker compose file.
- YAML
services:
...
observer:
image: stellar/anchor-platform:latest
command: --stellar-observer
env_file:
- ./dev.env
volumes:
- ./config:/home
Polling for Received Payments
The Stellar Observer makes JSON-RPC requests to the Platform API whenever it detects payments received for transactions initiated by sending organizations, thus updating the transaction's transfer_received_at date-time.
Your business should periodically poll the GET /transactions Platform API endpoint to detect these updates. You can refer to the following example:
- bash
curl http://localhost:8080/transactions?sep=31&order_by=transfer_received_at&order=desc
The response will include a list of cross-border payment transactions initiated by sending organizations. This list will be ordered according to the time a payment was received for that transaction. For each transaction returned, your business should check whether or not it has already detected the payment for that transaction. If it has, you have detected all payments made to your account(s).
Updating Transaction Via JSON-RPC
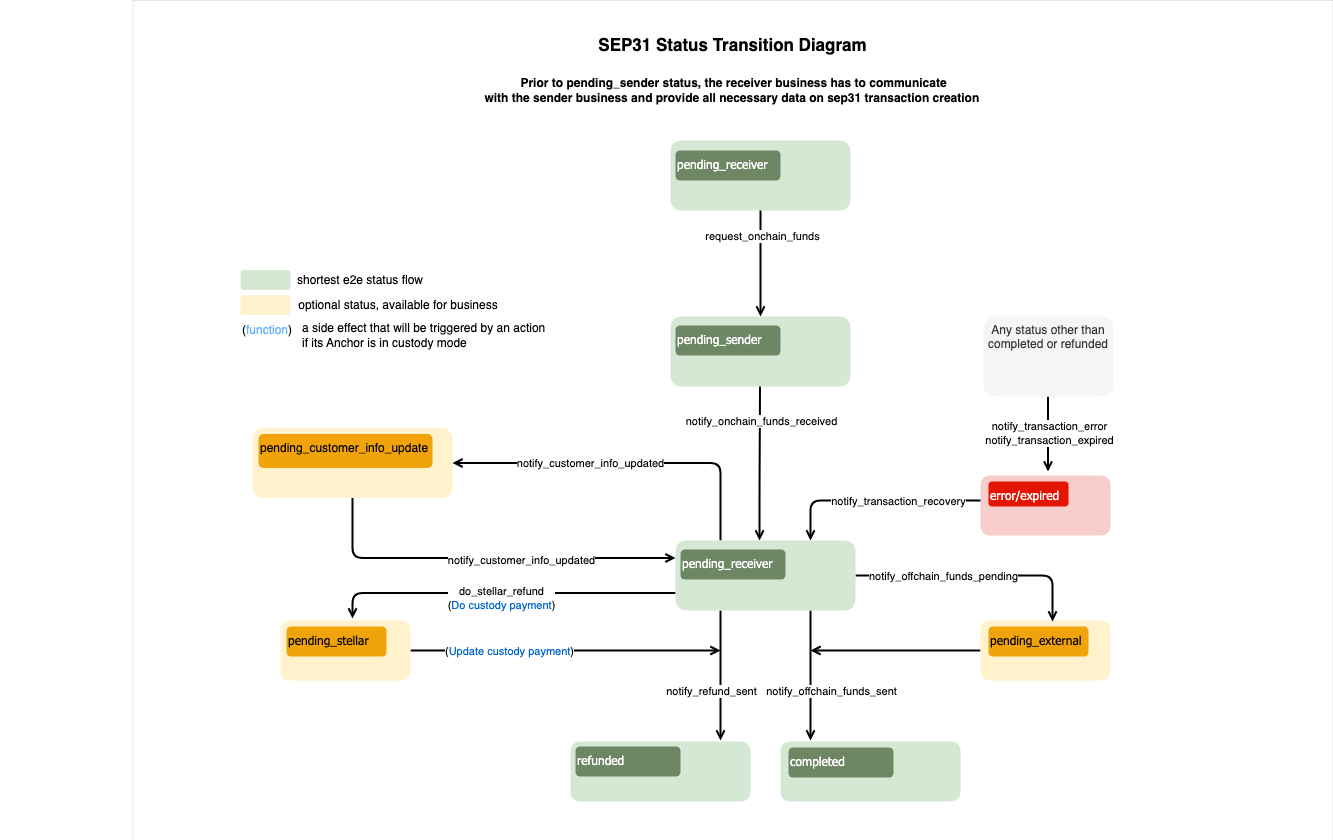
SEP-31 flow diagram defines sequence/rules of the transaction's status transition and a set of JSON-RPC methods that should be called to change that status. You can't define the status you want to set for a specific transaction in your requests. Each JSON-RPC method defines data structures that it expects in the request. If the request doesn't contain required attributes, the Anchor Platform will return an error and won't change the status of the transaction.
Statuses in green are mandatory and define the shortest flow.
Statuses in yellow are optional and can be skipped.
Statuses in red mean the transaction is in an error status or it has expired.
You can create a template for making a JSON-RPC requests to the Anchor Platform.
This chapter also contains information about the format of request/response and error codes that might be returned by the Anchor Platform.
Ready to Receive Funds
SEP-31 Transactions should initially be in the pending_receiver status. To request funds from the Sending Anchor, the Receiving Anchor should change the transaction status to pending_sender by making the following RPC request:
- JSON
// request-onchain-funds.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "request_onchain_funds",
"params": {
"transaction_id": "<transaction_id>",
"message": "Request onchain funds",
"destination_account": "GD...G",
"memo": "12345",
"memo_type": "id"
}
}
]
To execute this, you need to run:
- bash
./call-json-rpc.sh request-onchain-funds.json
The transaction status will be changed to pending_sender.
Funds Received
If the Sending Anchor has sent the funds, the Receiving Anchor should change the transaction status to pending_receiver by making the following JSON-RPC request:
- JSON
// onchain-funds-received.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "notify_onchain_funds_received",
"params": {
"transaction_id": "<transaction_id>",
"message": "Onchain funds received",
"stellar_transaction_id": "7...9",
"amount_in": {
"amount": 10
},
"amount_out": {
"amount": 9
},
"fee_details": {
"total": 1
}
}
}
]
To execute this, you need to run:
- bash
./call-json-rpc.sh onchain-funds-received.json
The transaction status will be changed to pending_receiver.
Offchain Funds Sent
To complete the transaction and change its status to completed, you need to make a notify_offchain_funds_sent JSON-RPC request.
- JSON
// offchain-funds-sent.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "notify_offchain_funds_sent",
"params": {
"transaction_id": "<transaction_id>",
"message": "Offchain funds sent",
"funds_sent_at": "2023-07-04T12:34:56Z",
"external_transaction_id": "a...c"
}
}
]
To execute this, you need to run:
- bash
./call-json-rpc.sh offchain-funds-sent.json
Offchain Funds Pending
Another option is to move the transaction's status to pending_external. This status means that payment has been submitted to external network, but it is not yet confirmed.
- JSON
// offchain-funds-pending.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "notify_offchain_funds_pending",
"params": {
"transaction_id": "<transaction_id>",
"message": "Offchain funds pending",
"external_transaction_id": "a...c"
}
}
]
To execute this, you need to run:
- bash
./call-json-rpc.sh offchain-funds-pending.json
Verifying Customer Information
In some cases, the Receiving Anchor might need to request an updated information from the Sending Anchor. For example, the bank tells the Receiving Anchor that the provided Receiving Client's name is incorrect or missing a middle initial. Since this information was sent via SEP-12, the transaction should go into the pending_customer_info_update status until the Sending Anchor makes another SEP-12 PUT /customer request to update. The Sending Anchor can check which fields need to be updated by making a SEP-12 GET /customer request including the id or account & memo parameters. The Receiving Anchor should respond with a NEEDS_INFO status and last_name included in the fields described.
After the Sending Anchor makes a SEP-12 PUT /customer request, call the notify_customer_info_updated JSON-RPC method againto update the transaction status. Additionally, call this method whenever the SEP-12 status for a customer changes, such as when the customer's information is being validated and the status changes from NEEDS_INFO to PROCESSING. This ensures that any clients configured with a callback URL are notified of the latest customer status, allowing the client to prompt the user to update their information.
- JSON
// notify-customer-info-updated.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "notify_customer_info_updated",
"params": {
"transaction_id": "<transaction_id>",
"message": "Customer info updated",
"customer_id": "45f8884d-d6e1-477f-a680-503179263359",
"customer_type": "sep31-receiver" // or sep31-sender
}
}
]
To execute this, you need to run:
- bash
./call-json-rpc.sh notify-customer-info-updated.json
Do Stellar Refund
Integration with the custody service allows you to do refund via custody service, such as Fireblocks.
- JSON
// do-stellar-refund.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "do_stellar_refund",
"params": {
"transaction_id": "<transaction_id>",
"message": "Do stellar refund",
"refund": {
"amount": {
"amount": 9,
"asset": "stellar:USDC:GBBD47IF6LWK7P7MDEVSCWR7DPUWV3NY3DTQEVFL4NAT4AQH3ZLLFLA5"
},
"amount_fee": {
"amount": 1,
"asset": "stellar:USDC:GBBD47IF6LWK7P7MDEVSCWR7DPUWV3NY3DTQEVFL4NAT4AQH3ZLLFLA5"
}
}
}
}
]
To execute this, you need to run:
- bash
./call-json-rpc.sh do-stellar-refund.json
You can't do multiple refunds in the SEP-31 flow. For this reason, the total refund amount plus the amount fee should equal amount_in. Otherwise, you will get an error.
Refund Sent
There is a possibility to send all funds back to the Sending Anchor (refund). You need to refund the whole sum(full refund).
- JSON
// refund-sent.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "notify_refund_sent",
"params": {
"transaction_id": "<transaction_id>",
"message": "Refund sent",
"refund": {
"id": "1c186184-09ee-486c-82a6-aa7a0ab1119c",
"amount": {
"amount": 10,
"asset": "iso4217:USD"
},
"amount_fee": {
"amount": 1,
"asset": "iso4217:USD"
}
}
}
}
]
To execute this, you need to run:
- bash
./call-json-rpc.sh refund-sent.json
You can't do multiple refunds in SEP-31 flow. For this reason, the amount to refund plus the amount fee should equal amount_in. Otherwise, you will get an error.
Transaction Error
If you encounter an unrecoverable error when processing the transaction, it's required to set the transaction status to error. You can use the message field to describe the details of the error.
- JSON
// transaction-error.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "notify_transaction_error",
"params": {
"transaction_id": "<transaction_id>",
"message": "Error occurred"
}
}
]
To execute this, you need to run:
- bash
./call-json-rpc.sh transaction-error.json
If a user has made a transfer, you should do a transaction recovery, and then you can retry processing the transaction or initiate a refund.
Expired Transaction
Your business may want to expire those transactions that have been abandoned by the user after some time. It's a good practice to clean up inactive transactions in the incomplete status. To do so, simply change the transaction's status to expired.
- JSON
// transaction-expired.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "notify_transaction_expired",
"params": {
"transaction_id": "<transaction_id>",
"message": "Transaction expired"
}
}
]
To execute this, you need to run:
- bash
./call-json-rpc.sh transaction-expired.json
This JSON-RPC method can't be used after the user has made a transfer.
Transaction Recovery
The transaction status can be changed from error/expired to pending-anchor. After recovery, you can refund the received assets or proceed with the processing of the transaction. To recover the transaction, it's necessary to make the following JSON-RPC request:
- JSON
// transaction-recovery.json
[
{
"id": 1,
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "notify_transaction_recovery",
"params": {
"transaction_id": "<transaction_id>",
"message": "Transaction recovered"
}
}
]
To execute this, you need to run:
- bash
./call-json-rpc.sh transaction-recovery.json
Configuration
You can enable these types of transactions by updating your assets.yaml file configuration:
- YAML
items:
- ...
sep31:
quotes_required: false