Pago por ruta
Un pago por ruta es donde el activo enviado puede ser diferente del activo recibido. Hay dos operaciones posibles de pago por ruta: 1) path_payment_strict_send, que permite al usuario especificar la cantidad del activo a enviar, y 2) path_payment_strict_receive, que permite al usuario especificar la cantidad del activo recibido. Lee más en la Guía de Pagos por Rutas.
Experiencia del usuario
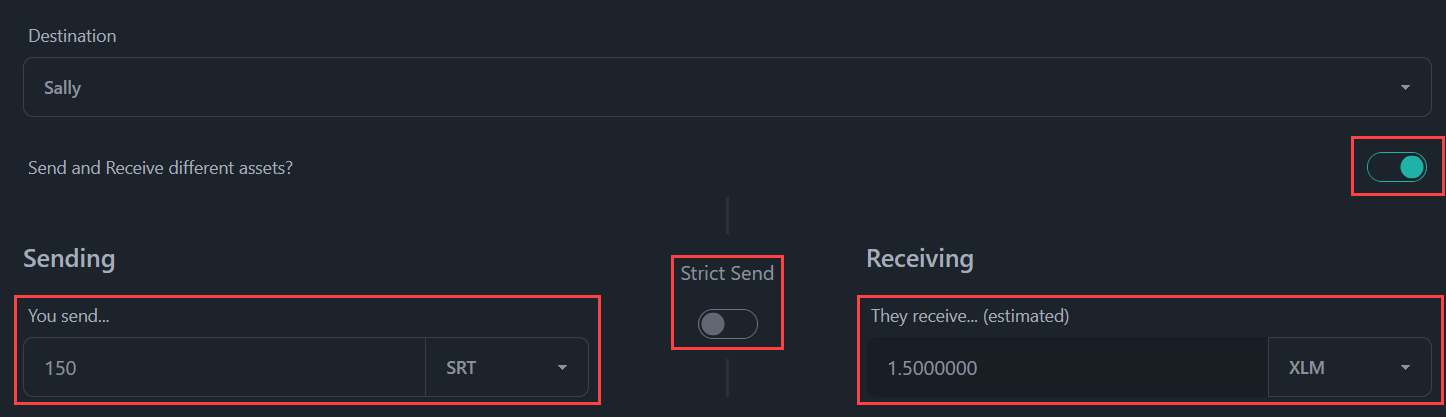
Con BasicPay, el usuario envía un pago por ruta navegando a la página de Pagos, donde puede seleccionar a un usuario de sus contactos o ingresar la clave pública de una dirección de destino. Luego selecciona el interruptor Enviar y Recibir Activos Diferentes y determina si quiere especificar el activo enviado o recibido. Finalmente selecciona el activo enviado y el activo recibido y las cantidades y selecciona el botón Vista Previa de Transacción.
The user will then preview the transaction, input their pincode, and select the Confirm button to sign and submit the transaction to the network.
Implementación del código
La página /dashboard/send
La mayoría de esta página se ha discutido en la sección de Pagos. A continuación, estamos destacando las piezas únicas que se agregan a BasicPay para permitir la función de pago por ruta.
<script>
// We import some of our `$lib` functions
import {
fetchAccount,
submit,
fetchAccountBalances,
findStrictSendPaths,
findStrictReceivePaths,
} from "$lib/stellar/horizonQueries";
import {
createCreateAccountTransaction,
createPathPaymentStrictReceiveTransaction,
createPathPaymentStrictSendTransaction,
createPaymentTransaction,
} from "$lib/stellar/transactions";
/* ... */
// Define some component variables that will be used throughout the page
let destination = "";
$: otherDestination = destination === "other";
let otherPublicKey = "";
let sendAsset = "native";
let sendAmount = "";
let receiveAsset = "";
let receiveAmount = "";
let memo = "";
let createAccount = null;
let pathPayment = false;
let availablePaths = [];
let strictReceive = false;
let paymentXDR = "";
let paymentNetwork = "";
/* ... */
// Query Horizon for available paths between a combination of source and destination assets and accounts.
const findPaths = async () => {
// Query the paths from Horizon
let paths = strictReceive
? await findStrictReceivePaths({
sourcePublicKey: data.publicKey,
destinationAsset: receiveAsset,
destinationAmount: receiveAmount,
})
: await findStrictSendPaths({
sourceAsset: sendAsset,
sourceAmount: sendAmount,
destinationPublicKey: otherDestination ? otherPublicKey : destination,
});
// Fill the component variable `availablPaths` with our returned paths
availablePaths = paths;
// If both send and receive assets have been selected re-select the path
// to update the relevant amount
if (receiveAsset && sendAsset) {
selectPath();
}
};
// Select a path for use in the path payment operation, and set the component variables accordingly.
const selectPath = () => {
if (strictReceive) {
// Set the `sendAmount` variable to the chosen path amount. The
// filtering we do checks if the asset_type matches because that
// will give us our 'native' XLM asset, otherwise we match on the
// asset_code.
sendAmount = availablePaths.filter(
(path) =>
path.source_asset_type === sendAsset ||
sendAsset.startsWith(path.source_asset_code),
)[0].source_amount;
} else {
// Set the `receiveAmount` variable to the chosen path amount. The
// filtering we do checks if the asset_type matches because that
// will give us our 'native' XLM asset, otherwise we match on the
// asset_code.
receiveAmount = availablePaths.filter(
(path) =>
path.destination_asset_type === receiveAsset ||
receiveAsset.startsWith(path.destination_asset_code),
)[0].destination_amount;
}
};
/* ... */
// Create a payment transaction depending on user selections, and present it to the user for approval or rejection.
const previewPaymentTransaction = async () => {
let transaction, network_passphrase
if (createAccount) {
{ transaction, network_passphrase } = await createCreateAccountTransaction({
/* ... */
})
} else if (pathPayment && strictReceive) {
{ transaction, network_passphrase } = await createPathPaymentStrictReceiveTransaction({
source: data.publicKey,
sourceAsset: sendAsset,
sourceAmount: sendAmount,
destination: otherDestination ? otherPublicKey : destination,
destinationAsset: receiveAsset,
destinationAmount: receiveAmount,
memo: memo,
})
} else if (pathPayment && !strictReceive) {
{ transaction, network_passphrase } = await createPathPaymentStrictSendTransaction({
source: data.publicKey,
sourceAsset: sendAsset,
sourceAmount: sendAmount,
destination: otherDestination ? otherPublicKey : destination,
destinationAsset: receiveAsset,
destinationAmount: receiveAmount,
memo: memo,
})
} else {
{ transaction, network_passphrase } = await createPaymentTransaction({
/* ... */
});
}
/* ... */
};
</script>
<!-- HTML has been omitted from this tutorial. Please check the source file -->
Fuente: https://github.com/stellar/basic-payment-app/blob/main/src/routes/dashboard/send/+page.svelte
Las funciones de transacción
En la sección anterior, usamos las funciones createPathPaymentStrictReceiveTransaction y createPathPaymentStrictSendTransaction. Estas se utilizan para crear transacciones que contienen la operación real de pago por ruta.
// Constructs and returns a Stellar transaction that will contain a path payment strict send operation to send/receive different assets.
export async function createPathPaymentStrictSendTransaction({
source,
sourceAsset,
sourceAmount,
destination,
destinationAsset,
destinationAmount,
memo,
}) {
// First, we setup our transaction by loading the source account from the
// network, and initializing the TransactionBuilder. This is the first step
// in constructing all Stellar transactions.
let server = new Server(horizonUrl);
let sourceAccount = await server.loadAccount(source);
let transaction = new TransactionBuilder(sourceAccount, {
networkPassphrase: networkPassphrase,
fee: maxFeePerOperation,
});
// We work out the assets to be sent by the source account and received by
// the destination account
let sendAsset =
sourceAsset === "native"
? Asset.native()
: new Asset(sourceAsset.split(":")[0], sourceAsset.split(":")[1]);
let destAsset =
destinationAsset === "native"
? Asset.native()
: new Asset(
destinationAsset.split(":")[0],
destinationAsset.split(":")[1],
);
// We will calculate an acceptable 2% slippage here for... reasons?
let destMin = ((98 * parseFloat(destinationAmount)) / 100).toFixed(7);
// If a memo was supplied, add it to the transaction
if (memo) {
transaction.addMemo(Memo.text(memo));
}
// Add a single `pathPaymentStrictSend` operation
transaction.addOperation(
Operation.pathPaymentStrictSend({
sendAsset: sendAsset,
sendAmount: sourceAmount.toString(),
destination: destination,
destAsset: destAsset,
destMin: destMin,
}),
);
// Before the transaction can be signed, it requires timebounds, and it must
// be "built"
let builtTransaction = transaction.setTimeout(standardTimebounds).build();
return {
transaction: builtTransaction.toXDR(),
network_passphrase: networkPassphrase,
};
}
// Constructs and returns a Stellar transaction that will contain a path payment strict receive operation to send/receive different assets.
export async function createPathPaymentStrictReceiveTransaction({
source,
sourceAsset,
sourceAmount,
destination,
destinationAsset,
destinationAmount,
memo,
}) {
// First, we setup our transaction by loading the source account from the
// network, and initializing the TransactionBuilder. This is the first step
// in constructing all Stellar transactions.
let server = new Server(horizonUrl);
let sourceAccount = await server.loadAccount(source);
let transaction = new TransactionBuilder(sourceAccount, {
networkPassphrase: networkPassphrase,
fee: maxFeePerOperation,
});
// We work out the assets to be sent by the source account and received by
// the destination account
let sendAsset =
sourceAsset === "native"
? Asset.native()
: new Asset(sourceAsset.split(":")[0], sourceAsset.split(":")[1]);
let destAsset =
destinationAsset === "native"
? Asset.native()
: new Asset(
destinationAsset.split(":")[0],
destinationAsset.split(":")[1],
);
/** @todo Figure out a good number to use for slippage. And why! And how to calculate it?? */
// We will calculate an acceptable 2% slippage here for... reasons?
let sendMax = ((100 * parseFloat(sourceAmount)) / 98).toFixed(7);
// If a memo was supplied, add it to the transaction
if (memo) {
transaction.addMemo(Memo.text(memo));
}
// Add a single `pathPaymentStrictSend` operation
transaction.addOperation(
Operation.pathPaymentStrictReceive({
sendAsset: sendAsset,
sendMax: sendMax,
destination: destination,
destAsset: destAsset,
destAmount: destinationAmount,
}),
);
// Before the transaction can be signed, it requires timebounds, and it must
// be "built"
let builtTransaction = transaction.setTimeout(standardTimebounds).build();
return {
transaction: builtTransaction.toXDR(),
network_passphrase: networkPassphrase,
};
}
Fuente: https://github.com/stellar/basic-payment-app/blob/main/src/lib/stellar/transactions.js